A sale conducted in accordance with the provisions of Section 363 of the United States Bankruptcy Code is referred to as a 363 sale. It can be something as simple as the office furniture or as extensive as almost all of an organization’s corporate assets. It contributes to the repayment of its debtors and lenders.

Explanation.
Section 363 of the legislation governing personal bankruptcy in the United States permits the debtor to sell part or nearly all of the debtor’s business assets outside of the debtor’s business, provided that certain conditions are met. It assists the debtor in raising finances so that they can settle their debts and pay off their creditors.
The 363 Sale process is a quicker and more robust way to acquire a buyer for asset sales, and it also avoids the depreciation of assets to a significant amount, which is a key benefit.
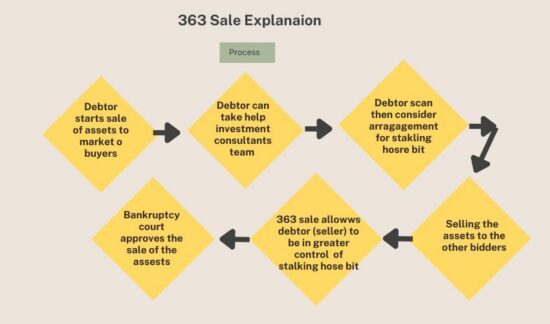
How Does 363 Sale Work?
Even though it is governed by the Code itself, the process is carried out in conjunction with the typical selling procedure. In order to get the process of 363 sales underway, either the debtor or the creditor has to submit a petition with the Code. The following are the stages that ultimately result in a sale:
The procedure is relatively simple and begins with the debtor initiating the sale of the assets in question to the potential market of buyers.
The debtor may seek the assistance of a group of investment advisors or bankers in order to sell the assets and draft the legal filing that will set forth the procedure of sale.
The creditor may then think about making an arrangement for a “stalking horse bid,” in which the minimum price is lowered intentionally so that potential bidders do not request for a lower price.
A debtor (seller) is able to exert a higher amount of control over a stalking horse offer through the use of a section 363 sale.
The other buyers in the market are allowed to participate in the bidding process once it has been successfully approved by the court (the court that oversees bankruptcies).
In order to ensure that the transaction is carried out in an open and honest manner, an auction is held after all offers have been received.
The person who places the highest offer wins the auction and is responsible for making the purchase.
Under any and all situations, the Court retains the discretion to either approve or reject the sale on the basis of reasonable adjustments and justifications provided by other bidders.
Example.
Let’s say that ABC Ltd. extended a loan of one million dollars to an American oil exploration company. After five years, the oil business had massive problems that left them unable to run the projects. A demand for debt repayment has been made by the creditor ABC Ltd. to the oil firm.
- The oil corporation submits a motion to the Bankruptcy Court as part of its legal strategy. The settlement was reached through the completion of 363 sales and is awaiting clearance from the court.
- The oil company’s assets will be valued at their utmost potential through a 363 sale, and this value will be correlated with the company’s obligations. Having evaluated all of the assets at $1.5 million, one of the debts is payable to ABC Ltd. for the amount of $1 million. The Court encourages bidders to increase the amount of their proposals while at the same time allowing oil executives to determine the amount of the “stalking horse” bid.
- The subsequent bids are taken in the form of an auction-style sale during the next step of the process, which occurs after the Court has agreed upon and accepted the stalking horse bid. The PPP business that submitted the highest bid will be awarded the right to make a claim on the assets.
- At each stage, the oil company and the PPP business are responsible for finishing the settlement and obtaining court permission. The PPP firm is responsible for the transfer of $1.5 million to the Oil firm. After then, it makes the payment of one million dollars that was owed to ABC Ltd.
Advantages.
- The 363 sale provides for out-of-court transactions, which help avoid the significant fees, delays, and other complications that are associated with the more involved and time-consuming process.
- It grants the debtor the ability to exercise a larger degree of control over the disposal of assets, which is not the case in a Chapter 7 liquidation sale, in which a trustee is given the responsibility of exercising control over the sale.
- Not only does the 363 sale benefit the creditor side, but it also benefits the debtor side by allowing the creditor side to raise questions and appeal to the courts in situations when the debtor side has a larger ask.
- A sale that is carried out in accordance with Section 363 and is done so correctly should be profitable for all parties involved.
Limitations.
- A 363 sale is, in every sense of the word, a public sale and makes an effort toward complete openness. Those customers who are unwilling to bid under such an open and honest procedure are excluded from the purchase.
- If there are a large number of potential purchasers interested in the item being sold, the process of establishing a stalking horse bid may become more difficult, and there is always the possibility of being outbid at any point.
- Because Section 363 of the United States Bankruptcy Code governs sales under this jurisdiction, the debtor is compelled to comply with virtually all of the legal conditions that have been specified. In the event that the debtor commits any violations or deviates from the terms of the agreement, the court has the authority to revoke or cancel the sale of assets and direct the debtor to ensure greater compliance.
- When a stalking horse offer takes place during one of these sale processes, it may necessitate more efforts for due diligence as well as concerns over charges.
- The fact that the lender only gives the debtor a finite amount of time to finish their due diligence is one of the most significant drawbacks associated with conducting.
Conclusion.
By making a claim under Section 363 of the United States Bankruptcy Code, debtors are given the ability to dispose of failing businesses and all of the assets associated with those businesses. Section 363 sales are distinct from Plan sales in that the primary objective of Section 363 transactions is to facilitate reorganization.
strategy that offers satisfactory recoveries of funds and resources to the parties that are owed money by the debtor. It is an effective tool for creditors to use in their pursuit of the maximum value for the assets at issue. Following the completion of the sale, the assets will be free and clear of any claims, liens, or other encumbrances.
Only in the event that the company has declared bankruptcy due to its inability to repay payments to its lenders is the section 363 sale of assets permissible. Nevertheless, it is in the best interest of every company that is contemplating filing for bankruptcy to carefully analyze the benefits and drawbacks of 363 sales in comparison to the Plan sale and credit bidding procedures.









